| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |

M-3SED 10 UK1X/350CG24N9K4
Rexroth
R900051053
Direct operated directional seat valve with solenoid actuation
Subplates (separate order)
Blocked connection is leak-tight
Reliable switching when under pressure over longer periods of standstill
Wet-pin DC solenoids with detachable coil (AC voltage possible by means of a rectifier)
Solenoid coil is rotatable by 90°
The coil can be changed without having to open the pressure-tight chamber
Electrical connection as individual connection
With concealed manual override, optional
Inductive position switch and proximity sensors (contactless)
Direct operated directional seat valve with solenoid actuation
Subplates (separate order)
Blocked connection is leak-tight
Reliable switching when under pressure over longer periods of standstill
Wet-pin DC solenoids with detachable coil (AC voltage possible by means of a rectifier)
Solenoid coil is rotatable by 90°
The coil can be changed without having to open the pressure-tight chamber
Electrical connection as individual connection
With concealed manual override, optional
Inductive position switch and proximity sensors (contactless)
3/2 directional seat valve
General
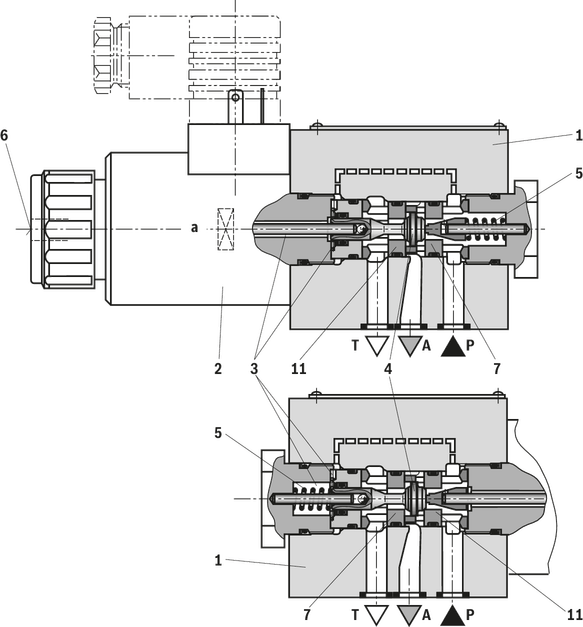
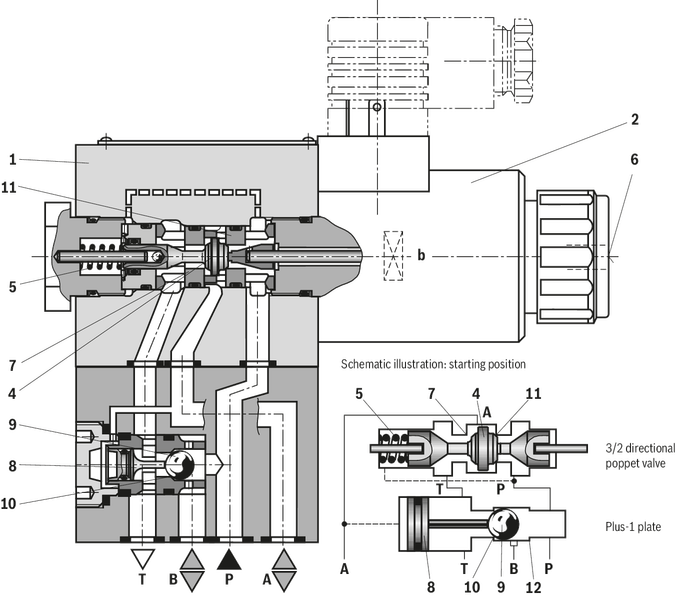
The directional valve of the type M-.SED is a direct operated directional seat valve with solenoid actuation. It controls the start, stop and direction of flow and mainly consists of a housing (1), the solenoid (2), the valve seats (7) and (11) as well as of the closing element (4).
The manual override (6) allows for the switching of the valve without solenoid energization.
Basic principle
The initial position of the valve (normally open "UK" or normally closed "CK") is determined by the arrangement of the spring (5). The chamber (3) behind the closing element (4) is connected to port P and sealed against port
T. Thus, the valve is pressure-compensated in relation to the actuating forces (solenoid and spring).
With the special closing element (4), ports P, A and T can be loaded with the maximum operating pressure (350 bar) and the flow can be directed into both directions (see symbols)!
In the initial position, the closing element (4) is pressed onto the seat (11) by the spring (5), in spool position, it is pressed onto the seat (7) by the solenoid (2). The flow is blocked in a leak-free manner.
With a sandwich plate, the Plus-1 plate, under the 3/2 directional seat valve, the function of a 4/2 directional seat valve is achieved.
Function of the Plus-1 plate
Initial position:
The main valve is not operated. The spring (5) holds the closing element (4) on the seat (11). Port P is blocked and A is connected to T. Apart from that, one control line is connected from A to the large area of the control spool (8), which is thus unloaded to the tank. The pressure applied via P now pushes the ball (9) onto the seat (10). Now, P is connected to B, and A to T.
Transition position:
Upon actuation of the main valve, the closing element (4) is shifted against the spring (5) and pressed onto the seat (7). During this, port T is blocked, while P, A, and B are briefly connected to each other.
Switching position:
P is connected to A. Since the pump pressure acts via A on the large area of the control spool (8), the ball (9) is pressed onto the seat (12). Thus, B is connected to T, and P to A. The ball (9) in the Plus-1 plate has a “positive spool overlap”.
Version “UK”

Version “CK”
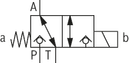
4/2 directional seat valve
General
The directional valve of the type M-.SED is a direct operated directional seat valve with solenoid actuation. It controls the start, stop and direction of flow and mainly consists of a housing (1), the solenoid (2), the valve seats (7) and (11) as well as of the closing element (4).
The manual override (6) allows for the switching of the valve without solenoid energization.
Basic principle
The initial position of the valve (normally open "UK" or normally closed "CK") is determined by the arrangement of the spring (5). The chamber (3) behind the closing element (4) is connected to port P and sealed against port
T. Thus, the valve is pressure-compensated in relation to the actuating forces (solenoid and spring).
With the special closing element (4), ports P, A and T can be loaded with the maximum operating pressure (350 bar) and the flow can be directed into both directions (see symbols)!
In the initial position, the closing element (4) is pressed onto the seat (11) by the spring (5), in spool position, it is pressed onto the seat (7) by the solenoid (2). The flow is blocked in a leak-free manner.
With a sandwich plate, the Plus-1 plate, under the 3/2 directional seat valve, the function of a 4/2 directional seat valve is achieved.
Function of the Plus-1 plate
Initial position:
The main valve is not operated. The spring (5) holds the closing element (4) on the seat (11). Port P is blocked and A is connected to T. Apart from that, one control line is connected from A to the large area of the control spool (8), which is thus unloaded to the tank. The pressure applied via P now pushes the ball (9) onto the seat (10). Now, P is connected to B, and A to T.
Transition position:
Upon actuation of the main valve, the closing element (4) is shifted against the spring (5) and pressed onto the seat (7). During this, port T is blocked, while P, A, and B are briefly connected to each other.
Switching position:
P is connected to A. Since the pump pressure acts via A on the large area of the control spool (8), the ball (9) is pressed onto the seat (12). Thus, B is connected to T, and P to A. The ball (9) in the Plus-1 plate has a “positive spool overlap”.
Attention!
In order to avoid pressure intensification when using differential cylinders, the annulus area of the cylinder must be connected at A.
The use of the Plus-1 plate and the seat arrangement offer the following options:
Version “D”
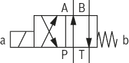
Version “Y”
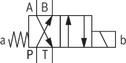
Type M-4SED 10 Y1X/350CG24N9K4
The use of a throttle insert is required if, due to prevailing operating conditions, flows which exceed the performance limit of the valve can occur during the switching processes.
Examples:
Accumulator operation,
use as pilot control valve with internal pilot fluid tapping.
3/2 directional seat valve
The throttle insert is inserted into port P of the seat valve.
4/2 directional seat valve
The throttle insert is inserted into port P of the Plus-1 plate
The check valve insert allows a free flow from P to A and closes A to P in a leak-free form.
3/2 directional seat valve
The check valve insert is inserted into port P of the seat valve.
4/2 directional seat valve
The check valve insert is inserted into port P of the Plus-1 plate.
3/2 directional seat valve
General
The directional valve of the type M-.SED is a direct operated directional seat valve with solenoid actuation. It controls the start, stop and direction of flow and mainly consists of a housing (1), the solenoid (2), the valve seats (7) and (11) as well as of the closing element (4).
The manual override (6) allows for the switching of the valve without solenoid energization.
Basic principle
The initial position of the valve (normally open "UK" or normally closed "CK") is determined by the arrangement of the spring (5). The chamber (3) behind the closing element (4) is connected to port P and sealed against port
T. Thus, the valve is pressure-compensated in relation to the actuating forces (solenoid and spring).
With the special closing element (4), ports P, A and T can be loaded with the maximum operating pressure (350 bar) and the flow can be directed into both directions (see symbols)!
In the initial position, the closing element (4) is pressed onto the seat (11) by the spring (5), in spool position, it is pressed onto the seat (7) by the solenoid (2). The flow is blocked in a leak-free manner.
With a sandwich plate, the Plus-1 plate, under the 3/2 directional seat valve, the function of a 4/2 directional seat valve is achieved.
Function of the Plus-1 plate
Initial position:
The main valve is not operated. The spring (5) holds the closing element (4) on the seat (11). Port P is blocked and A is connected to T. Apart from that, one control line is connected from A to the large area of the control spool (8), which is thus unloaded to the tank. The pressure applied via P now pushes the ball (9) onto the seat (10). Now, P is connected to B, and A to T.
Transition position:
Upon actuation of the main valve, the closing element (4) is shifted against the spring (5) and pressed onto the seat (7). During this, port T is blocked, while P, A, and B are briefly connected to each other.
Switching position:
P is connected to A. Since the pump pressure acts via A on the large area of the control spool (8), the ball (9) is pressed onto the seat (12). Thus, B is connected to T, and P to A. The ball (9) in the Plus-1 plate has a “positive spool overlap”.
Version “UK”

Version “CK”

4/2 directional seat valve
General
The directional valve of the type M-.SED is a direct operated directional seat valve with solenoid actuation. It controls the start, stop and direction of flow and mainly consists of a housing (1), the solenoid (2), the valve seats (7) and (11) as well as of the closing element (4).
The manual override (6) allows for the switching of the valve without solenoid energization.
Basic principle
The initial position of the valve (normally open "UK" or normally closed "CK") is determined by the arrangement of the spring (5). The chamber (3) behind the closing element (4) is connected to port P and sealed against port
T. Thus, the valve is pressure-compensated in relation to the actuating forces (solenoid and spring).
With the special closing element (4), ports P, A and T can be loaded with the maximum operating pressure (350 bar) and the flow can be directed into both directions (see symbols)!
In the initial position, the closing element (4) is pressed onto the seat (11) by the spring (5), in spool position, it is pressed onto the seat (7) by the solenoid (2). The flow is blocked in a leak-free manner.
With a sandwich plate, the Plus-1 plate, under the 3/2 directional seat valve, the function of a 4/2 directional seat valve is achieved.
Function of the Plus-1 plate
Initial position:
The main valve is not operated. The spring (5) holds the closing element (4) on the seat (11). Port P is blocked and A is connected to T. Apart from that, one control line is connected from A to the large area of the control spool (8), which is thus unloaded to the tank. The pressure applied via P now pushes the ball (9) onto the seat (10). Now, P is connected to B, and A to T.
Transition position:
Upon actuation of the main valve, the closing element (4) is shifted against the spring (5) and pressed onto the seat (7). During this, port T is blocked, while P, A, and B are briefly connected to each other.
Switching position:
P is connected to A. Since the pump pressure acts via A on the large area of the control spool (8), the ball (9) is pressed onto the seat (12). Thus, B is connected to T, and P to A. The ball (9) in the Plus-1 plate has a “positive spool overlap”.
Attention!
In order to avoid pressure intensification when using differential cylinders, the annulus area of the cylinder must be connected at A.
The use of the Plus-1 plate and the seat arrangement offer the following options:
Version “D”
Version “Y”
Type M-4SED 10 Y1X/350CG24N9K4

The use of a throttle insert is required if, due to prevailing operating conditions, flows which exceed the performance limit of the valve can occur during the switching processes.
Examples:
Accumulator operation,
use as pilot control valve with internal pilot fluid tapping.
3/2 directional seat valve
The throttle insert is inserted into port P of the seat valve.
4/2 directional seat valve
The throttle insert is inserted into port P of the Plus-1 plate
The check valve insert allows a free flow from P to A and closes A to P in a leak-free form.
3/2 directional seat valve
The check valve insert is inserted into port P of the seat valve.
4/2 directional seat valve
The check valve insert is inserted into port P of the Plus-1 plate.
01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | |
DB | 5X | / | * |
01 | Pressure relief valve | DB |
02 | Without directional valve | no code |
03 | Pilot-operated valve (complete) | no code |
Pilot control valve without main spool insert (do not enter any size) | C | |
Pilot control valve with main spool insert (enter size 10 or 30) | C | |
Pilot control valve without main spool insert for subplate mounting (do not enter any size) | T 1) | |
04 | Size 10 | |
Subplate mounting "no code" | 10 | |
Threaded connection "G" | 10 (G1/2) | |
Size 16 | ||
Threaded connection "G" | 15 (G3/4) | |
Size 25 | ||
Subplate mounting "no code" | 20 | |
Threaded connection "G" | 20 (G1) | |
Threaded connection "G" | 25 (G1 1/4) | |
Size 32 | ||
Subplate mounting "no code" | 30 | |
Threaded connection "G" | 30 (G1 1/2) | |
05 | Without directional valve | no code |
Type of connection | ||
06 | Subplate mounting or cartridge valve | no code |
For threaded connection | G | |
Adjustment type for pressure adjustment | ||
07 | Rotary knob (not for version "C" and "T") | 1 |
Sleeve with hexagon and protective cap | 2 | |
Lockable rotary knob with scale | 3 2) | |
Rotary knob with scale | 7 | |
08 | Main spool Ø24 mm (all sizes) | – |
Main spool Ø28 mm (only for NG32) | N | |
09 | Component series 50 … 59 (50 … 59: unchanged installation and connection dimensions) | 5X |
10 | Set pressure up to 50 bar | 50 |
Set pressure up to 100 bar | 100 | |
Set pressure up to 200 bar | 200 | |
Set pressure up to 315 bar | 315 | |
Set pressure up to 350 bar | 350 | |
Pilot oil flow | ||
11 | External pilot oil supply, internal pilot oil return | X 3) |
Internal pilot oil supply, external pilot oil return | Y | |
Pilot oil supply and pilot oil return external | XY 3) | |
12 | Standard version | no code |
Valve for minimum cracking pressure (not for versions "without main spool insert" and not suitable for mutual relief) | U 4) | |
13 | Without switching shock damping | no code |
14 | Without directional valve | no code |
15 | Without directional valve | no code |
16 | Without manual override | no code |
Electrical connection | ||
17 | Without directional valve | no code |
18 | Without directional valve | no code |
Corrosion resistance | ||
19 | None | no code |
Improved corrosion protection (240 h salt spray test according to EN ISO 9227) | J3 5) | |
Seal material | ||
20 | NBR seals | no code |
FKM seals | V | |
Observe compatibility of seals with hydraulic fluid used. (Other seals upon request) | ||
Equipment Directive | ||
21 | Without type-examination procedure | no code |
Type-examination tested safety valve according to Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU | E | |
22 | Further details in the plain text | * |
| 1) | DBT corresponds to DBC, however with closed central bore |
| 2) | H-Key with material no. R900008158 is included in the scope of delivery. |
| 3) | Not with version "DBC" |
| 4) | Only possible up to pressure rating 315 bar |
| 5) | Only version "2", however without protective cap |
(Component series 5X according to Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU)
NG | Type designation | Component marking | Maximum flow qVmaxin l/min with pilot oil return | Set response overpressure p in bar | |
external "Y" | internal "–" | ||||
10 |  | TÜV.SV.▢ – 851.12.F.G.p | 170 230 230 230 | 130 200 200 200 | 30 ... 60 61 ... 110 111 ... 210 211 ... 350 |
25 |  | TÜV.SV.▢ – 852.22.F.G.p | 250 270 420 450 | 180 210 320 400 | 30 ... 60 61 ... 110 111 ... 210 211 ... 350 |
32 |  | TÜV.SV.▢ – 853.32.F.G.p | 600 600 650 700 | 225 340 540 580 | 30 ... 60 61 ... 110 111 ... 210 211 ... 350 |
1 | For subplate mounting | no code |
For threaded connection | G | |
Adjustment type for pressure adjustment | ||
2 | Hand wheel (pressure adjustment sealed, unloading or setting of a lower response pressure possible!) | 1 |
With sealed protective cap (no adjustment/unloading possible) | 2 | |
Pressure | ||
3 | To be entered by the customer, e.g. pressure adjustment ≥ 30 bar and possible in 5 bar steps. | e.g. 150 |
Pilot oil flow | ||
4 | Pilot oil supply internal, pilot oil return internal | no code |
Pilot oil supply internal, pilot oil return external (Recommendation) | Y 1) | |
5 | NBR seals | no code |
FKM seals | V | |
▢ | Value entered at the factory | |
| 1) | Pilot oil supply external "X" not possible |
01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | |
DB | 5X | / | * |
01 | Pressure relief valve | DB |
02 | Without directional valve | no code |
03 | Pilot-operated valve (complete) | no code |
Pilot control valve without main spool insert (do not enter any size) | C | |
Pilot control valve with main spool insert (enter size 10 or 30) | C | |
Pilot control valve without main spool insert for subplate mounting (do not enter any size) | T 1) | |
04 | Size 10 | |
Subplate mounting "no code" | 10 | |
Threaded connection "G" | 10 (G1/2) | |
Size 16 | ||
Threaded connection "G" | 15 (G3/4) | |
Size 25 | ||
Subplate mounting "no code" | 20 | |
Threaded connection "G" | 20 (G1) | |
Threaded connection "G" | 25 (G1 1/4) | |
Size 32 | ||
Subplate mounting "no code" | 30 | |
Threaded connection "G" | 30 (G1 1/2) | |
05 | Without directional valve | no code |
Type of connection | ||
06 | Subplate mounting or cartridge valve | no code |
For threaded connection | G | |
Adjustment type for pressure adjustment | ||
07 | Rotary knob (not for version "C" and "T") | 1 |
Sleeve with hexagon and protective cap | 2 | |
Lockable rotary knob with scale | 3 2) | |
Rotary knob with scale | 7 | |
08 | Main spool Ø24 mm (all sizes) | – |
Main spool Ø28 mm (only for NG32) | N | |
09 | Component series 50 … 59 (50 … 59: unchanged installation and connection dimensions) | 5X |
10 | Set pressure up to 50 bar | 50 |
Set pressure up to 100 bar | 100 | |
Set pressure up to 200 bar | 200 | |
Set pressure up to 315 bar | 315 | |
Set pressure up to 350 bar | 350 | |
Pilot oil flow | ||
11 | External pilot oil supply, internal pilot oil return | X 3) |
Internal pilot oil supply, external pilot oil return | Y | |
Pilot oil supply and pilot oil return external | XY 3) | |
12 | Standard version | no code |
Valve for minimum cracking pressure (not for versions "without main spool insert" and not suitable for mutual relief) | U 4) | |
13 | Without switching shock damping | no code |
14 | Without directional valve | no code |
15 | Without directional valve | no code |
16 | Without manual override | no code |
Electrical connection | ||
17 | Without directional valve | no code |
18 | Without directional valve | no code |
Corrosion resistance | ||
19 | None | no code |
Improved corrosion protection (240 h salt spray test according to EN ISO 9227) | J3 5) | |
Seal material | ||
20 | NBR seals | no code |
FKM seals | V | |
Observe compatibility of seals with hydraulic fluid used. (Other seals upon request) | ||
Equipment Directive | ||
21 | Without type-examination procedure | no code |
Type-examination tested safety valve according to Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU | E | |
22 | Further details in the plain text | * |
| 1) | DBT corresponds to DBC, however with closed central bore |
| 2) | H-Key with material no. R900008158 is included in the scope of delivery. |
| 3) | Not with version "DBC" |
| 4) | Only possible up to pressure rating 315 bar |
| 5) | Only version "2", however without protective cap |
(Component series 5X according to Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU)
NG | Type designation | Component marking | Maximum flow qVmaxin l/min with pilot oil return | Set response overpressure p in bar | |
external "Y" | internal "–" | ||||
10 |  | TÜV.SV.▢ – 851.12.F.G.p | 170 230 230 230 | 130 200 200 200 | 30 ... 60 61 ... 110 111 ... 210 211 ... 350 |
25 |  | TÜV.SV.▢ – 852.22.F.G.p | 250 270 420 450 | 180 210 320 400 | 30 ... 60 61 ... 110 111 ... 210 211 ... 350 |
32 |  | TÜV.SV.▢ – 853.32.F.G.p | 600 600 650 700 | 225 340 540 580 | 30 ... 60 61 ... 110 111 ... 210 211 ... 350 |
1 | For subplate mounting | no code |
For threaded connection | G | |
Adjustment type for pressure adjustment | ||
2 | Hand wheel (pressure adjustment sealed, unloading or setting of a lower response pressure possible!) | 1 |
With sealed protective cap (no adjustment/unloading possible) | 2 | |
Pressure | ||
3 | To be entered by the customer, e.g. pressure adjustment ≥ 30 bar and possible in 5 bar steps. | e.g. 150 |
Pilot oil flow | ||
4 | Pilot oil supply internal, pilot oil return internal | no code |
Pilot oil supply internal, pilot oil return external (Recommendation) | Y 1) | |
5 | NBR seals | no code |
FKM seals | V | |
▢ | Value entered at the factory | |
| 1) | Pilot oil supply external "X" not possible |
Size | 10 | ||
Weight | 3/2 directional seat valve | kg | 2.6 |
4/2 directional seat valve | kg | 3.9 | |
Installation position | any | ||
Ambient temperature range | NBR seals | °C | -30 … +50 |
FKM seals | °C | -20 … +50 | |
Hydraulic fluid | Classification | Suitable sealing materials | Standards | |
Mineral oil | HL, HLP | FKM, NBR | DIN 51524 | |
Bio-degradable | Insoluble in water | HEES (synthetic esters) | FKM | VDMA 24568 |
HETG (rape seed oil) | FKM, NBR | |||
Soluble in water | HEPG (polyglycols) | FKM | VDMA 24568 | |
Other hydraulic fluids on request | ||||
electrical
Voltage type | Direct voltage | AC voltage | ||
Available voltages | V | 12 / 24 / 42 / 96 / 110 / 205 / 220 1) | 110 / 120 / 230 | |
Voltage tolerance (nominal voltage) | % | ± 10 | ||
Power consumption | W | 30 | ||
Duty cycle | % | 100 | ||
Switching time according to ISO 6403 | ON | ms | 20 … 50 | |
OFF (without rectifier) | ms | 5 … 25 | ||
OFF (with rectifier) | ms | 30 … 50 | ||
Maximum switching frequency | 1/h | 15000 | ||
Protection class according to EN 60529 | IP65 (If a suitable and a correctly mounted mating connector are used.) | |||
Maximum coil temperature | °C | 150 | ||
| 1) | Other voltages upon request |
In the electrical connection, the protective earthing conductor (PE, grounded) is to be connected in accordance with the stipulations.
The electric connection is realized via a 4-pole mating connector (separate order) with connection thread M12 x 1.
Connection voltage (DC voltage) | V | 24 | ||
Voltage tolerance (connection voltage) | +30 %/-15 % | |||
Admissible residual ripple | % | ≤ 10 | ||
Max. load capacity | mA | 400 | ||
Switching outputs 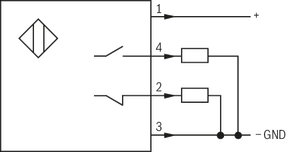 | PNP transistor outputs, load between switching outputs and GND | |||
Pinout  | 1 | V | 24 | |
2, 4 | Switching output | mA | 400 | |
3 | Earthing (GND) | V | 0 | |
M12x1 plug-in connections 1) | K72L | ||
Available voltages 2) | V | 24 | |
Limited switch-off voltage peak | V | -44 … -55 | |
Voltage tolerance (nominal voltage) | % | ± 10 | |
Power consumption | W | 30 | |
Duty cycle | % | 100 | |
Switching time according to ISO 6403 | ON | ms | 30 … 50 |
OFF (without rectifier) | ms | 10 … 20 | |
OFF (with rectifier) | ms | 35 … 45 | |
Maximum switching frequency | Standard | 1/h | 15000 |
Protection class according to EN 60529 3) | IP65 | ||
Protection class according to DIN EN 61140 | III | ||
Maximum coil temperature 4) | °C | 150 | |
| 1) | Mating connectors according to IEC 60947-5-2, separate order, see data sheet 08006 |
| 2) | Connection to functional low voltage with secure separation only = PELV/SELV |
| 3) | Only with the use of the mating connectors indicated by us and with correct installation. |
| 4) | Due to the surface temperatures of the solenoid coils, the standards ISO 13732-1 and EN 982 need to be adhered to! |
Size | 10 | ||
Maximum operating pressure | Port P | bar | 350 |
Port A | bar | 350 | |
Port B | bar | 350 | |
Maximum flow | l/min | 40 | |
Hydraulic fluid | see table | ||
Hydraulic fluid temperature range | NBR seals | °C | -30 … +80 |
FKM seals | °C | -20 … +80 | |
Viscosity range | mm²/s | 2.8 … 500 | |
Maximum admissible degree of contamination of the hydraulic fluid, cleanliness class according to ISO 4406 (c) 1) | Class 20/18/15 according to ISO 4406 (c) | ||
| 1) | The cleanliness classes specified for the components must be adhered to in hydraulic systems. Effective filtration prevents faults and simultaneously increases the life cycle of the components. For the selection of the filters, see www.boschrexroth.com/filter. |
Size | 10 | ||
Weight | 3/2 directional seat valve | kg | 2.6 |
4/2 directional seat valve | kg | 3.9 | |
Installation position | any | ||
Ambient temperature range | NBR seals | °C | -30 … +50 |
FKM seals | °C | -20 … +50 | |
Hydraulic fluid | Classification | Suitable sealing materials | Standards | |
Mineral oil | HL, HLP | FKM, NBR | DIN 51524 | |
Bio-degradable | Insoluble in water | HEES (synthetic esters) | FKM | VDMA 24568 |
HETG (rape seed oil) | FKM, NBR | |||
Soluble in water | HEPG (polyglycols) | FKM | VDMA 24568 | |
Other hydraulic fluids on request | ||||
electrical
Voltage type | Direct voltage | AC voltage | ||
Available voltages | V | 12 / 24 / 42 / 96 / 110 / 205 / 220 1) | 110 / 120 / 230 | |
Voltage tolerance (nominal voltage) | % | ± 10 | ||
Power consumption | W | 30 | ||
Duty cycle | % | 100 | ||
Switching time according to ISO 6403 | ON | ms | 20 … 50 | |
OFF (without rectifier) | ms | 5 … 25 | ||
OFF (with rectifier) | ms | 30 … 50 | ||
Maximum switching frequency | 1/h | 15000 | ||
Protection class according to EN 60529 | IP65 (If a suitable and a correctly mounted mating connector are used.) | |||
Maximum coil temperature | °C | 150 | ||
| 1) | Other voltages upon request |
In the electrical connection, the protective earthing conductor (PE, grounded) is to be connected in accordance with the stipulations.
The electric connection is realized via a 4-pole mating connector (separate order) with connection thread M12 x 1.
Connection voltage (DC voltage) | V | 24 | ||
Voltage tolerance (connection voltage) | +30 %/-15 % | |||
Admissible residual ripple | % | ≤ 10 | ||
Max. load capacity | mA | 400 | ||
Switching outputs  | PNP transistor outputs, load between switching outputs and GND | |||
Pinout  | 1 | V | 24 | |
2, 4 | Switching output | mA | 400 | |
3 | Earthing (GND) | V | 0 | |
M12x1 plug-in connections 1) | K72L | ||
Available voltages 2) | V | 24 | |
Limited switch-off voltage peak | V | -44 … -55 | |
Voltage tolerance (nominal voltage) | % | ± 10 | |
Power consumption | W | 30 | |
Duty cycle | % | 100 | |
Switching time according to ISO 6403 | ON | ms | 30 … 50 |
OFF (without rectifier) | ms | 10 … 20 | |
OFF (with rectifier) | ms | 35 … 45 | |
Maximum switching frequency | Standard | 1/h | 15000 |
Protection class according to EN 60529 3) | IP65 | ||
Protection class according to DIN EN 61140 | III | ||
Maximum coil temperature 4) | °C | 150 | |
| 1) | Mating connectors according to IEC 60947-5-2, separate order, see data sheet 08006 |
| 2) | Connection to functional low voltage with secure separation only = PELV/SELV |
| 3) | Only with the use of the mating connectors indicated by us and with correct installation. |
| 4) | Due to the surface temperatures of the solenoid coils, the standards ISO 13732-1 and EN 982 need to be adhered to! |
Size | 10 | ||
Maximum operating pressure | Port P | bar | 350 |
Port A | bar | 350 | |
Port B | bar | 350 | |
Maximum flow | l/min | 40 | |
Hydraulic fluid | see table | ||
Hydraulic fluid temperature range | NBR seals | °C | -30 … +80 |
FKM seals | °C | -20 … +80 | |
Viscosity range | mm²/s | 2.8 … 500 | |
Maximum admissible degree of contamination of the hydraulic fluid, cleanliness class according to ISO 4406 (c) 1) | Class 20/18/15 according to ISO 4406 (c) | ||
| 1) | The cleanliness classes specified for the components must be adhered to in hydraulic systems. Effective filtration prevents faults and simultaneously increases the life cycle of the components. For the selection of the filters, see www.boschrexroth.com/filter. |
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

1.2 | Solenoid "b" |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
12 | Valve mounting bores |
1.1 | Solenoid “a” |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
12 | Valve mounting bores |
4 hexagon socket head cap screws
ISO 4762 - M6 x 40 - 10.9-flZn-240h-L
friction coefficient μtotal = 0.09 to 0.14,
tightening torque MA = 12.5 Nm ± 10%,
material no. R913000058
Subplates (separate order)
G 66/01 (G3/8)
G 67/01 (G1/2)
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

| 1) | Only version "T" |
1.2 | Solenoid "b" |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
12 | Valve mounting bores |
1.1 | Solenoid “a” |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
12 | Valve mounting bores |
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

1.1 | Solenoid “a” |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
9 | Plus-1 plate |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
13 | Valve mounting screws see dimensions |
4 hexagon socket head cap screws
ISO 4762 - M6 x 40 - 10.9-flZn-240h-L
friction coefficient μtotal = 0.09 to 0.14,
tightening torque MA = 12.5 Nm ± 10%,
material no. R913000059
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

1.2 | Solenoid "b" |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
9 | Plus-1 plate |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
13 | Valve mounting screws see dimensions |
Dimensions in mm

| 1) | only NG150 |
Dimensions in mm

| 1) | For dimensions, see valve dimensions |
The dimensions are nominal dimensions which are subject to tolerances.
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

1.2 | Solenoid "b" |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
12 | Valve mounting bores |
1.1 | Solenoid “a” |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
12 | Valve mounting bores |
4 hexagon socket head cap screws
ISO 4762 - M6 x 40 - 10.9-flZn-240h-L
friction coefficient μtotal = 0.09 to 0.14,
tightening torque MA = 12.5 Nm ± 10%,
material no. R913000058
Subplates (separate order)
G 66/01 (G3/8)
G 67/01 (G1/2)
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

| 1) | Only version "T" |
1.2 | Solenoid "b" |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
12 | Valve mounting bores |
1.1 | Solenoid “a” |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
12 | Valve mounting bores |
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

1.1 | Solenoid “a” |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
9 | Plus-1 plate |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
13 | Valve mounting screws see dimensions |
4 hexagon socket head cap screws
ISO 4762 - M6 x 40 - 10.9-flZn-240h-L
friction coefficient μtotal = 0.09 to 0.14,
tightening torque MA = 12.5 Nm ± 10%,
material no. R913000059
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm

1.2 | Solenoid "b" |
2.1 | Dimension for solenoid with concealed manual override “N9” |
2.2 | Dimension for solenoid without manual override |
3 | Mating connector without circuitry (separate order) |
4 | Mating connector with circuitry (separate order) |
5 | Space required to remove the coil |
6 | Name plate |
7 | Attention! With 3/2 directional seat valves, ports B and TB are available as blind counterbores. With 4/2 directional seat valves, port TB is available as blind counterbore. |
8 | Identical seal rings for ports A, B, and T; seal ring for port P |
9 | Plus-1 plate |
10 | Space required to remove the coil |
11 | |
13 | Valve mounting screws see dimensions |
Dimensions in mm

| 1) | only NG150 |
Dimensions in mm

| 1) | For dimensions, see valve dimensions |
The dimensions are nominal dimensions which are subject to tolerances.
Dimensions in mm

Dimensions in mm
